

Where your skin cancer begins determines its type and your treatment options. Melanocytes produce more melanin when you're in the sun to help protect the deeper layers of your skin. Melanocytes - which produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its normal color - are located in the lower part of your epidermis.Basal cells, which produce new skin cells, sit beneath the squamous cells.Squamous cells lie just below the outer surface and function as the skin's inner lining.The epidermis contains three main types of cells: The epidermis is a thin layer that provides a protective cover of skin cells that your body continually sheds. Skin cancer begins in your skin's top layer - the epidermis.

The mutations cause the cells to grow out of control and form a mass of cancer cells. Skin cancer occurs when errors (mutations) occur in the DNA of skin cells. Melanoma, another type of skin cancer, arises in the pigment cells (melanocytes). As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, where a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma can occur. One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. Skin cancer begins in the cells that make up the outer layer (epidermis) of your skin. Your doctor will investigate your skin changes to determine a cause. Not all skin changes are caused by skin cancer. Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice any changes to your skin that worry you. Sebaceous gland carcinomas - which usually appear as hard, painless nodules - can develop anywhere, but most occur on the eyelid, where they're frequently mistaken for other eyelid problems. This uncommon and aggressive cancer originates in the oil glands in the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is most often found on the head, neck and trunk. Merkel cell carcinoma causes firm, shiny nodules that occur on or just beneath the skin and in hair follicles. Other people with an increased risk of Kaposi sarcoma include young men living in Africa or older men of Italian or Eastern European Jewish heritage. Kaposi sarcoma mainly occurs in people with weakened immune systems, such as people with AIDS, and in people taking medications that suppress their natural immunity, such as people who've undergone organ transplants. This rare form of skin cancer develops in the skin's blood vessels and causes red or purple patches on the skin or mucous membranes.
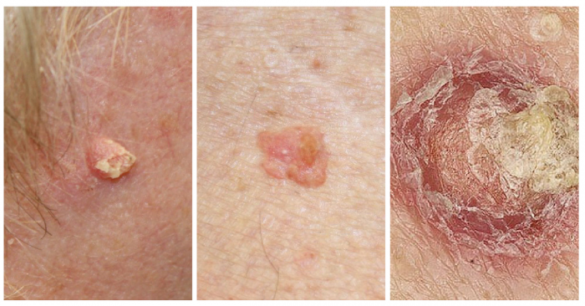
Other, less common types of skin cancer include: Signs and symptoms of less common skin cancers


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
